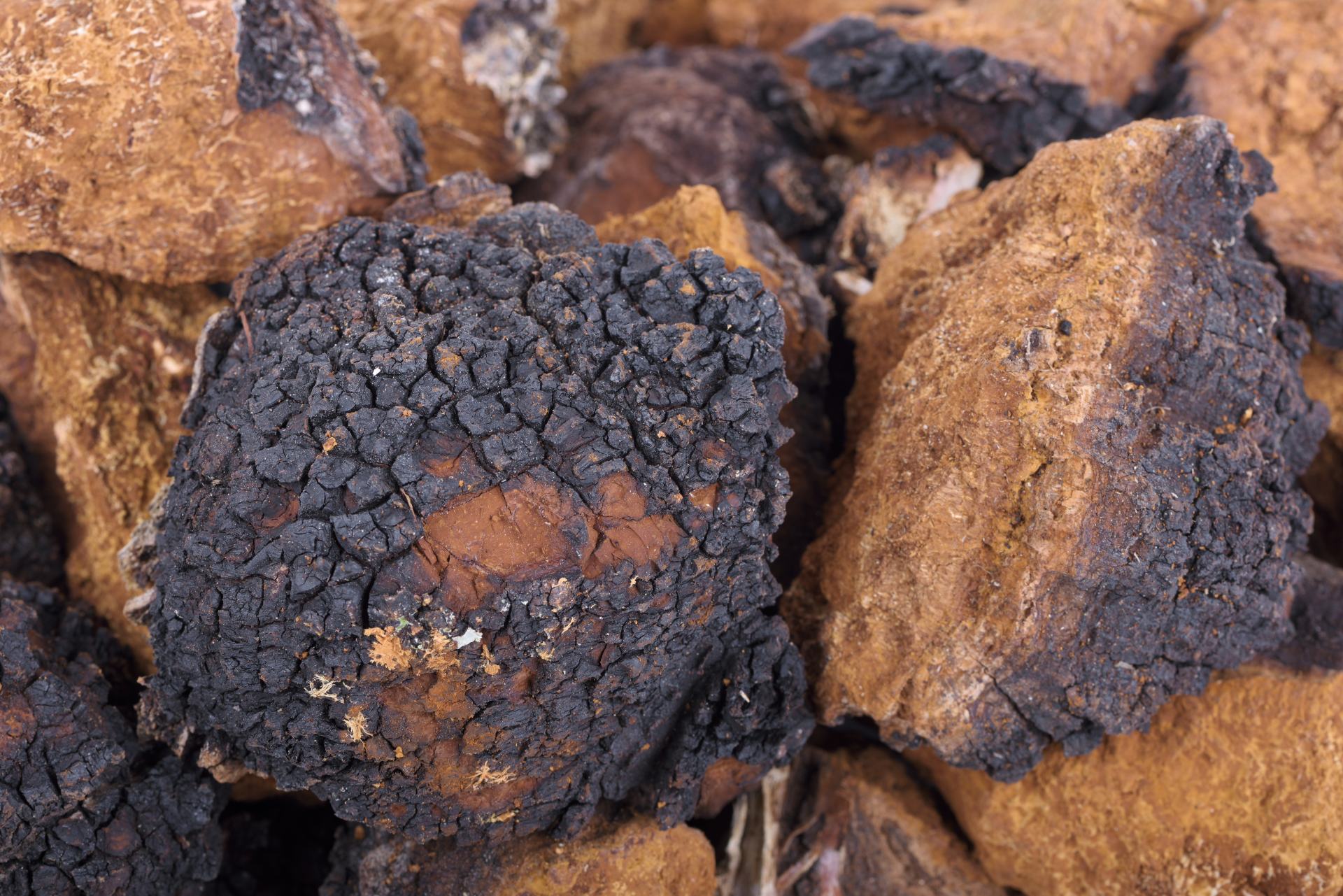
Chaga (Inonotus obliquus), is a parasitic fungus that grows on tree trunks, mainly birches. In recent years, interest in chaga has increased significantly due to its unique medicinal properties and active components that can have a positive effect on human health. This article discusses the medical and biological properties of chaga, the biology of this mushroom and its chemical composition, which will help to better understand its potential in pharmacology and medicine.
- Biology of the chaga mushroom
1.1 Taxonomy and ecology
Chaga (Inonotus obliquus) belongs to the Hymenochaetaceae family and is a wood parasite that affects deciduous trees, mainly birch (Betula). It is also found on alder, rowan and maple. The infection process begins with the penetration of fungal spores through damaged tree bark. Chaga mycelium grows into the wood, causing slow destruction of tree tissue and the formation of a characteristic black, coal-black growth on the surface – a sterile form of the fungus.
1.2 Morphological features
Chaga has several morphological phases. The main and visible part of the fungus is a hard, cortical body of irregular shape, often resembling a coal growth. This is not a fruiting body, but a sterile form of the fungus, which can develop on the tree for many years. Fruiting bodies, which form spores, grow inside the trunk and are less noticeable. The inner part of the growth is yellow-brown, while the outer surface is dark and has a structure resembling coal.
1.3 Life cycle
Chaga is a perennial parasite. It grows in the body of the tree until it leads to the death of the tree. However, chaga continues to develop on the dead tree, producing its fruiting bodies inside the dead wood, which facilitates further dissemination of spores. The entire life cycle of the fungus can take from 10 to 20 years, depending on environmental conditions.
- Chemical composition of the chaga mushroom
Chaga is valued for its unique bioactive components. The main active substances are:
2.1 Polyphenols and melanins
Chaga contains high concentrations of polyphenolic compounds that have powerful antioxidant properties. Antioxidants are important for protecting cells from oxidative stress, which is associated with the development of many chronic diseases, including cancer and cardiovascular pathologies. The external black color of chaga is due to the presence of melanin, a pigment that is also known for its protective properties, including photoprotection and antioxidant activity.
2.2 Triterpenes and sterols
Chaga contains a wide range of triterpenes and sterols, including betulin and betulinic acid. Betulin gets into chaga from the birch tree on which the fungus lives. Betulinic acid attracts the attention of scientists due to its antiviral, anticancer and anti-inflammatory properties.
2.3 Polysaccharides and beta-glucans
Chaga is rich in polysaccharides, such as β-glucans, which have an immunostimulating and anticancer effect. These compounds promote the activation of macrophages and other components of the immune system, which helps the body fight infections and tumor cells. They also have a positive effect on the regulation of blood sugar levels and lipid metabolism.
2.4 Minerals and microelements
Chaga is also rich in minerals such as potassium, calcium, magnesium, iron, manganese, zinc and copper. These elements are necessary for maintaining the normal functioning of the body and ensuring metabolic processes.
- Biomedical properties of Chaga
Chaga has been used in traditional medicine for many centuries, especially in Russia, China and Northern Europe. Modern research confirms its therapeutic potential.
3.1 Anti-cancer properties
One of the most interesting aspects of Chaga is its potential anti-tumor effect. Studies have shown that betulinic acid and other compounds of the fungus can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) in cancer cells and inhibit their growth. In vitro and in vivo experiments have shown that Chaga extracts have activity against various types of cancer, including lung, breast, liver and colon cancer.
3.2 Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties
The high antioxidant content of Chaga makes it a powerful tool for combating oxidative stress, which is one of the causes of aging and the development of chronic diseases. In addition, Chaga extracts have anti-inflammatory properties, making it a promising treatment for inflammatory diseases such as arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease.
3.3 Immunostimulating effect
Chaga polysaccharides, especially β-glucans, have a powerful stimulating effect on the immune system, activating macrophages, natural killers and other components of the innate immune system. This makes chaga a promising tool for the prevention of infectious diseases and improving the overall health of the immune system.
3.4 Antiviral properties
Chaga demonstrates antiviral activity against some viruses, including the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and herpes virus. Experimental studies have shown that mushroom extracts can inhibit viral replication and reduce their pathogenicity.
3.5 Anti-inflammatory effect
Chaga extracts demonstrate anti-inflammatory action, which can be useful in the treatment of inflammatory diseases such as arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease and various infections.
3.6 Normalization of blood sugar levels
Chaga can positively affect blood sugar levels, making it useful for patients with type 2 diabetes. The mushroom’s polysaccharides help improve insulin sensitivity and lower glucose levels.
3.7 Liver protection
The antioxidants in chaga help protect liver cells from damage caused by toxins, infections, and stress. Chaga may be useful in the prevention and treatment of liver diseases, including hepatitis and fatty liver disease.
3.8 Normalizing blood pressure and cholesterol
Chaga may have a positive effect on lipid metabolism and reduce the level of “bad” cholesterol (LDL), which reduces the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Chaga also helps normalize blood pressure.
3.9 Improving the nervous system
Some active compounds in chaga may have a calming effect and reduce stress. Chaga may help improve sleep quality and normalize the psychoemotional state.
3.10 Antiviral and antibacterial action
Chaga extracts exhibit antiviral and antibacterial activity, which makes it useful for the prevention and treatment of infectious diseases, including influenza and other viral infections.
3.11 Anti-ulcer agent
Some studies show that chaga can protect the stomach lining from damage and promote ulcer healing. This is due to its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
- Biohacking and Chaga
Biohacking is the practice of actively intervening in the body to optimize its functions. This may include:
- Dietary changes: using superfoods, supplements, and special diets.
- Physical activity: choosing optimal workouts to improve strength, endurance, and cognitive functions.
- Biomonitoring: using gadgets to track health (fitness trackers, sugar meters, blood tests).
- Mental practices: meditation, mindfulness techniques, breathing exercises.
- Experimenting with supplements: adaptogens, nootropics, and other means to improve cognitive and physical activity.
The goal of biohacking is to achieve maximum efficiency of the body and mind, track your health, and adjust it based on data.
Chaga in the context of biohacking can be considered one of the natural remedies for improving the overall health of the body. Biohackers often experiment with various adaptogens, and chaga is one of the most popular supplements due to its proven properties of supporting the immune system, improving energy, and reducing inflammation.
As such, chaga is a natural product that can be integrated into a biohacking practice to improve physical and mental well-being.
- Forms of use:
- Decoctions and infusions: a traditional way of using chaga to improve immunity and treat gastrointestinal diseases.
- Extracts: used in pharmaceuticals and dietary supplements for systemic support of the body.
- Cryo powder: highly digestible pharmaceutical powder.
- Cosmetics: creams and ointments with chaga are used to treat skin diseases and improve skin condition.
Chaga is actively studied by modern science, and although its potential is great, it is important to take into account the individual characteristics of the body and consult a doctor before use, especially in the presence of serious diseases.
- Anti-aging effect of Chaga.
Antioxidants: Chaga is rich in antioxidants such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), melanin, polyphenols and beta-glucans. Antioxidants help neutralize free radicals, unstable molecules that damage cells and accelerate the aging process.
Stimulates immunity: Chaga stimulates the immune system thanks to beta-glucans and other active substances, which helps maintain the health of cells and tissues, slowing down their destruction.
Skin protection: Chaga extract can help protect the skin from ultraviolet radiation and other external factors, preventing the formation of wrinkles and age-related pigment spots. Melanin contained in chaga can also protect the skin from photoaging.
Rejuvenating effect on cells: Chaga helps restore damaged cells and improve their function, which helps slow down the biological aging of the body. Supports Healthy Metabolism: Chaga may help support metabolism and hormonal balance, which may have a positive effect on overall health and the body’s ability to resist age-related changes. Regular use of chaga in supplements or extracts may have anti-aging effects by supporting healthy skin, improving immunity, and protecting cells from damage, which slows the aging process.
Conclusion
Chaga (Inonotus obliquus) deserves its place among the “kings” of medicinal mushrooms due to its unique biology and rich chemical composition. Its biologically active components have a wide range of therapeutic effects, including anticancer, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and immunostimulating properties. Modern scientific research confirms the feasibility of using chaga as a promising source of biologically active substances for the development of new drugs and supplements. In the future, more clinical studies will be needed to fully unlock the potential of this mushroom and integrate it into modern medicine.
References
- Zhang, L., & Zheng, Y. (2019). Medicinal mushroom Inonotus obliquus (Chaga): Nutritional value and medical characteristics. Journal of Nutrition & Medicine, 10(4), 202-210.
- Shashkina, M. Y., Shashkin, P. N., & Sergeev, A. V. (2006). Chemical and medicobiological properties of chaga (review). Pharmaceutical Chemistry Journal, 40(10), 560-568.
- Patel, S., & Goyal, A. (2012). Recent developments in mushrooms as anti-cancer therapeutics: a review. 3 Biotech, 2(1), 1-15.
Author: Dr. Petr Mělník, doctor of integral medicine