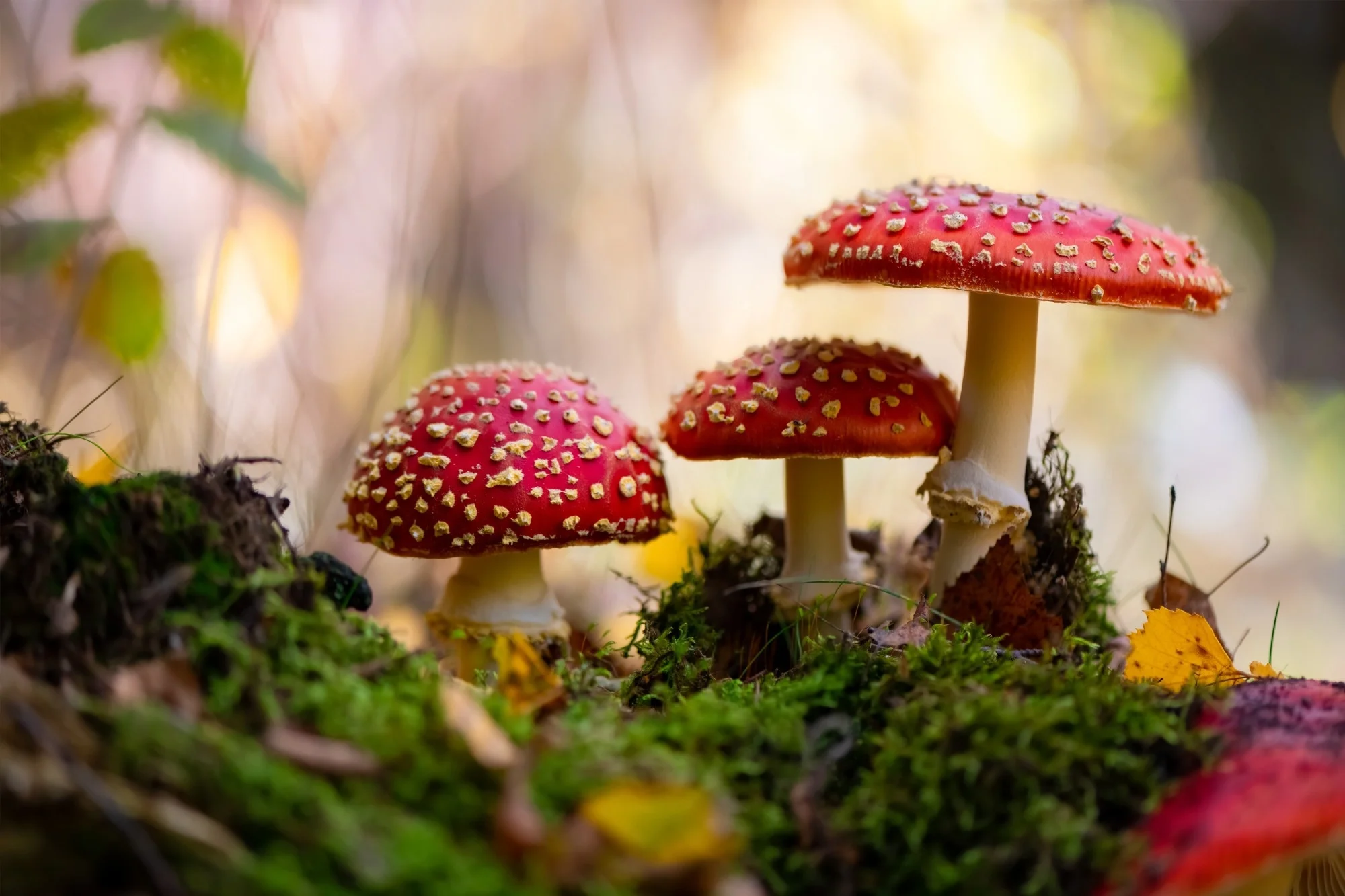
In recent years, interest in the medicinal properties of the Amanita muscaria mushroom has increased significantly, especially in countries such as Canada, where research is being conducted into the use of this mushroom in the treatment of alcoholism and smoking addiction. The fly agaric mushroom has long been used in shamanic and healing practices by indigenous peoples of Siberia and Scandinavia, but only recently has the scientific community begun to study its therapeutic potential more closely. Among the many potential uses of the mushroom, its effects on the nervous system have proven particularly interesting, which may be useful in the treatment of addictions.
In Canada, several years ago, the red fly agaric (amanita muscaria) was officially recommended for the production of dietary supplements. https://webprod.hc-sc.gc.ca/nhpid-bdipsn/searchIngred
Main Active Ingredients and Their Effects on the Body
The key active ingredients of Amanita muscaria are ibotenic acid and muscimol. These compounds affect GABA receptors in the brain, which may cause changes in perception, reduced anxiety, and improved mood. It is this effect on the nervous system that is considered a potential mechanism for helping to combat addictions.
Research conducted in Canada has shown that properly dosed preparations based on Amanita muscaria can reduce cravings for alcohol and nicotine. Scientists have found that due to the interaction of muscimol with receptors associated with the feeling of pleasure, patients experience less desire to repeatedly drink alcohol or smoke.
Examples of successful use
Case study 1: An experiment was conducted in Vancouver involving a group of people suffering from chronic alcoholism. One of the participants was a 42-year-old man who had been abusing alcohol for 15 years. After a three-month course of microdosing with Amanita muscaria, the patient reported a significant decrease in cravings for alcohol. It is important to note that during the therapy, he began to feel an improvement in mood and a decrease in anxiety, which played an important role in his success. Six months after completing the therapy, the man continued to abstain from alcohol.
Case Study 2: Another study conducted in Toronto used a similar approach to treat smoking addiction. A 35-year-old woman who had smoked for 20 years began a course of microdosing fly agaric for eight weeks. After the first month, she experienced a decrease in the number of cigarettes she smoked, and after two months, she completely quit smoking. According to the patient, the mushroom helped her cope with anxiety and stress, which had previously pushed her to smoke.
Mechanism of action in the fight against alcohol and smoking
The main mechanism of action of Amanita muscaria in the fight against addictions is its ability to stabilize the activity of neurons in the areas of the brain responsible for motivation and pleasure. Research shows that substances contained in fly agaric can restore the balance of neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin, which reduces the need for artificial stimulants of pleasure such as alcohol and nicotine.
An important aspect is also its effect on GABA receptors, which play a key role in the regulation of anxiety and stress. Since many people abuse alcohol and smoking in an attempt to cope with negative emotions, fly agaric can act as an alternative remedy that helps manage these conditions without bad habits.
Side effects and risks
Despite promising results, fly agaric is a mushroom with potentially toxic properties, and its use requires a cautious approach. If the wrong dosage is taken, ibotenic acid can cause hallucinations, nausea and headaches. Therefore, any attempts to use fly agaric for medicinal purposes should be carried out under the supervision of a doctor or a specialist with experience in the field of psychopharmacology and herbal medicines.
In addition, there have not yet been long-term clinical studies to fully assess the long-term effects of Amanita muscaria in the treatment of addictions. However, the results of the first stages of research are encouraging, and interest in this area of therapy continues to grow.
Conclusions
Amanita muscaria, previously known primarily for its hallucinogenic properties, opens up new prospects in the treatment of alcohol and nicotine addiction. Research conducted in Canada shows that microdosing of fly agaric can effectively reduce cravings for alcohol and smoking by affecting the nervous system and the regulation of neurotransmitters responsible for pleasure and motivation. Although further research is needed, this approach may become an important part of complex therapy for people seeking to get rid of bad habits.
It is important to remember that the use of fly agaric for medicinal purposes should only be carried out under the supervision of specialists, given its potential toxicity and possible side effects.
Author: Dr. Petr Mělník, doctor of integral medicine